Table of Contents
Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons is a compound which is consist of hydrogen and carbon both, hydrogen is the first element of the periodic table while carbon is the sixth element of the periodic table. You can also say that “the combination of carbon and hydrogen makes many compounds called hydrocarbons”. Example:- CH3, C2H5, Cyclopropane.
Sources of hydrocarbons
These are the main sources of hydrocarbons
1. Natural gas:- natural gas is the basic source of hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbon are very flammable and produce carbon dioxide, water and heat when burned.
2. Coal:- Coal is the basic source of hydrocarbons. When coal is burnt, the gases that are released are hydrocarbons. So that’s the sources of hydrocarbons.
3. Petroleum:- Petroleum is actually a source of hydrocarbons. The basic compounds of petroleum are hydrocarbons.
Classification of hydrocarbons
Basically hydrocarbons is divided into three major parts; saturated hydrocarbons, unsaturated hydrocarbons and aromatic hydrocarbons.
1. Saturated hydrocarbons
Saturated hydrocarbons have carbon – carbon single bond. Single bond is a requirement that is called the saturated hydrocarbons. It can also be compound of ring chain or compound of straight chain. Basically, alkanes are called saturated hydrocarbons, which have the general formula CnH2n+2.
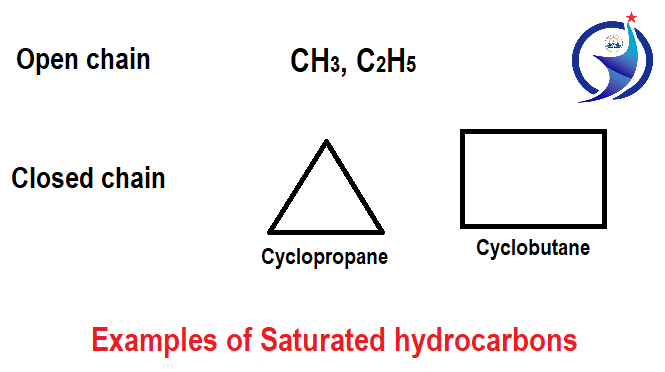
Saturated hydrocarbons are divided into two major parts; open chain hydrocarbons and closed chain hydrocarbons. Open chain hydrocarbons are where carbon atoms are interrelated either linearly or branching so that molecules have an open chain structure. This compound is also called aliphatic compounds. Closed chain hydrocarbons are where carbon atoms are present in cyclic form or ring form. At least three carbons are required to form closed chain hydrocarbon. If the number of carbons is less than 3 then closed chain hydrocarbons cannot be formed.
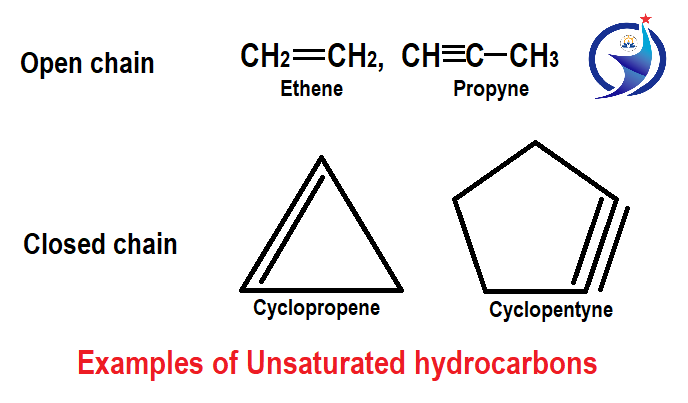
2. Unsaturated hydrocarbons
Unsaturated hydrocarbons have carbon – carbon multiple bonds. Basically, it consists of alkenes and alkynes because alkenes have carbon-carbon double bonds and alkynes have carbon-carbon triple bonds. The general formula of alkenes and alkynes are CnH2n and CnH2n-2. In this also both the compound of straight chain and compound of closed chain are present.
Cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbon are those where carbon atoms are present in a cyclic form or ring form, where carbon to carbon are attached to each other with the help of double and triple bonds.
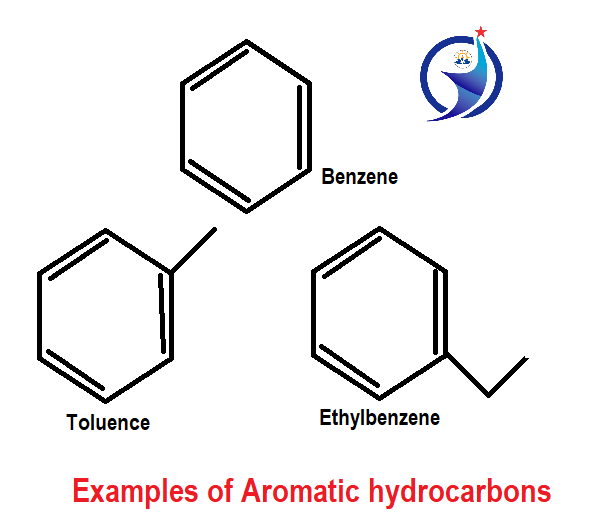
3. Aromatic hydrocarbons
Aromatic hydrocarbons contain at least one hexagonal ring with alternating double bond. The basic example of aromatic hydrocarbon is benzene. Benzene, Toluene and ethylbenzene; these are the simple examples of aromatic hydrocarbon.

Hi mimprovement.com owner, Your posts are always insightful and valuable.