Table of Contents
Alkanes
Alkanes are also known as PARAFFINS because of their low reactivity. PARAFFINS is composed of two words; parium and affinis, while ‘parium’ means little and ‘affinis’ means reactivity. Alkanes have carbon-carbon single bond. It has low activity due to saturation. The general formula of saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon is CnH2n+2. The hybridization of alkanes is sp3.
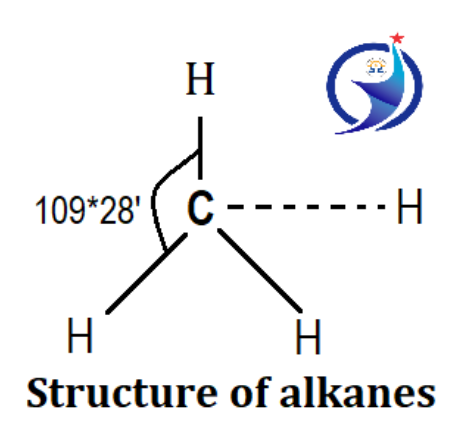
Structure of alkanes
All saturated hydrocarbons have a carbon-to-carbon single bond, so their structure is tetrahedral. The angle between the tetrahedral structure is 109°28′.
Preparation of alkanes
These are some important and easy methods for preparations of alkanes:-
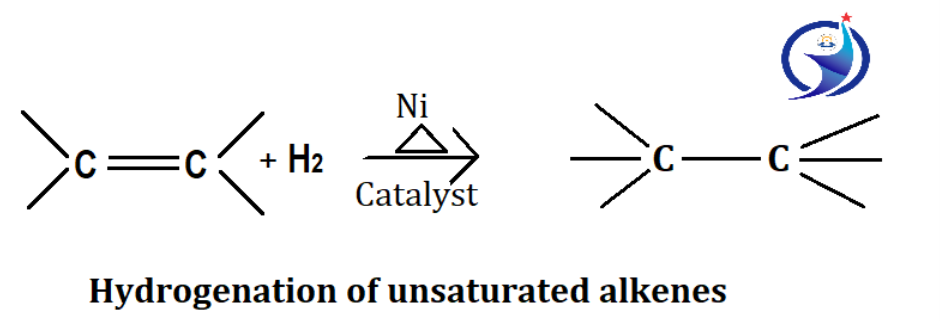
1. By hydrogenation of unsaturated alkene
This is the addition of hydrogen on unsaturated alkenes or alkynes. In this process we can use Ni/Pt as a catalyst. For hydrogenation Pt/H2 can also be used as the catalyst.
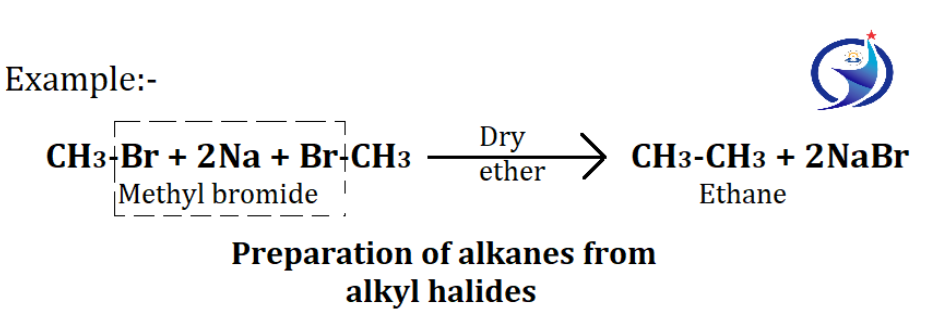
2. From alkyl halides
Alkanes are obtained with the help of Wurtz reaction in alkyl halides. Reaction of alkyl halides with sodium in dry ether to give a symmetrical alkane with twice the number of carbon atoms.
Condition of wurtz reaction: – First, This method is preferably suitable only for the preparation of symmetrical alkane and second Usually only one type of alkyl halides is used.
3. By reduction of alkyl halides
Alkyl halides are reduced to form alkane. Reduction means addition of hydrogen. This reduction is complete in the presence of zinc and HCl which act as a reducing agent because whenever metals and acids are reacted, H2 gas is released which helps in reduction.
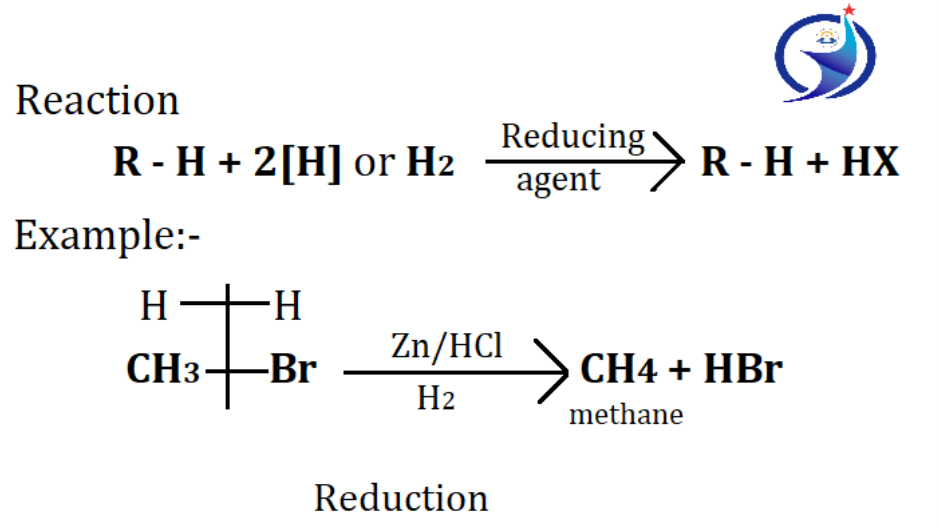
✓ Reducing agents for reduction of alkyl halides:-
a) Zn/HCl
b) H2 in presence of red phosphorus
c) Hl in presence of red phosphorus
d) Zn-Cu couple and alcohol
e) LiAIH4 and NaBH4
All these reducing agents reduce alkyl halide and convert it into alkane.
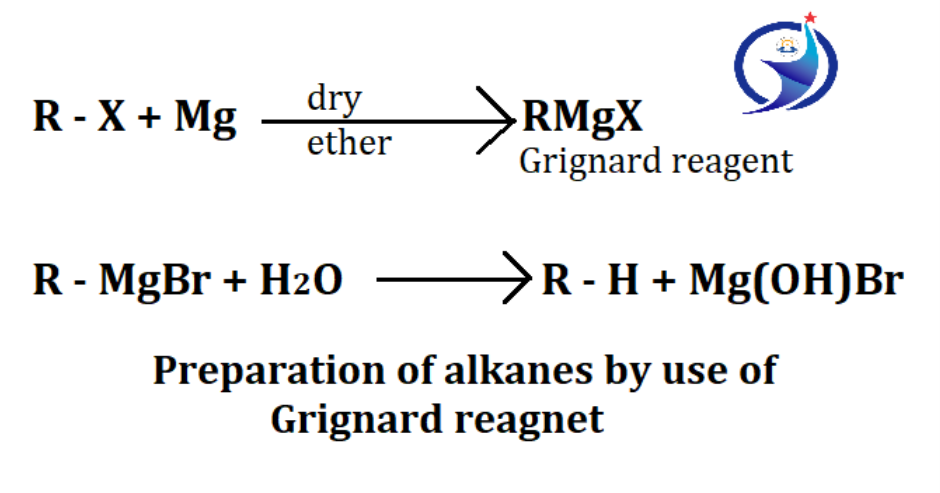
4. By use of Grignard reagent
Grignard reagent is an organometallic compound which is highly reactive. Organometallic compound is composed of metal and carbon atom, while carbon atom has negative charge and element has positive charge. For the formation of organometallic compounds, alkyl halides are reacted with magnesium in the presence of dry ether. The resulting compound is also called Grignard reagent. When Grignard reagent is reacted with water, alkane is formed. Grignard reagent is highly reactive and easily decomposed by water
Physical properties of alkanes
- Non-polar: – Alkanes are nonpolar due to which its reactivity is very low. why alkanes non-polar? Because very little difference in electronegativity between carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- Boiling point: – Alkanes have a boiling point directly proportional to the molar mass. As the molar mass of alkanes increases, its boiling point also increases. In alkanes there is anti -proportional branching of the boiling point. As soon as branching of alkanes is done, then its surface area gets worked out.
- Melting point: – the melting point of Alkanes also increase with the increase in molar mass but the increase is not so regular. Alkanes with even number of carbons have more melting point than odd carbon alkanes.
- Solubility: – Alkanes are non-polar so they like to dissolve in nonpolar. As like ether, benzene, Ccl4.
- Density: – Alkanes are the least dense amongst organic compound.

Dear mimprovement.com webmaster, Well done!
Hello mimprovement.com owner, Thanks for the educational content!
Hi mimprovement.com owner, Thanks for the informative post!