Table of Contents
Organization and function of ANS
Nervous comes from brain and spinal cord and bind with different organs. They release different neurotransmitter and control the function of organ. They study of release of neurotransmitter and their function on different organ is called autonomic nervous system.
Autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s internal balance and regulating various involuntary functions. It is a complex network of nerves and ganglia that controls automatic processes such as heart rate, digestion, breathing, and hormonal secretion.
The organization of the ANS is divided into two main branches: the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). The SNS is responsible for activating the body’s “fight or flight” response, preparing it for action in response to stress or danger. On the other hand, the PNS works to counterbalance this response by promoting relaxation and conserving energy during restful states.
The function of the ANS is to maintain homeostasis within the body by constantly monitoring and adjusting various physiological processes. For example, when faced with a stressful situation, such as encountering a predator, the SNS triggers an increase in heart rate, dilation of blood vessels, and release of stress hormones like adrenaline. Conversely, during rest or sleep, the PNS slows down heart rate, constricts blood vessels, and promotes digestion.
Autonomic nervous system involves involuntary responses(movement) of our body. It further divided into two parts:
1. Sympathetic nervous system
Those system which active in abnormal situation of body and maintain the body. In this type of ANA, the ganglionic junction is present away to the organ. In this system preganglionic fiber is short and past ganglionic fiber is long. They release transmitter is inhibitory in nature, adrenaline bind with three types of receptors: Alpha, Bita and Gama.
2. Parasympathetic nervous system
In this type of nervous system, our body come back to normal condition after any abnormal situation, it is also help in maintain the homeostasis of body such as increase digestion rate and normal heart rate.
In this type of autonomic nervous system, the ganglionic junction is present near to the organ in this system preganglionic fiber is long and past ganglionic fiber is small. They release acetylcholine neurotransmitter which is excitatory in nature. Acetylcholine binds with two types of receptors: N-nicotinic and M-Muscarinic.
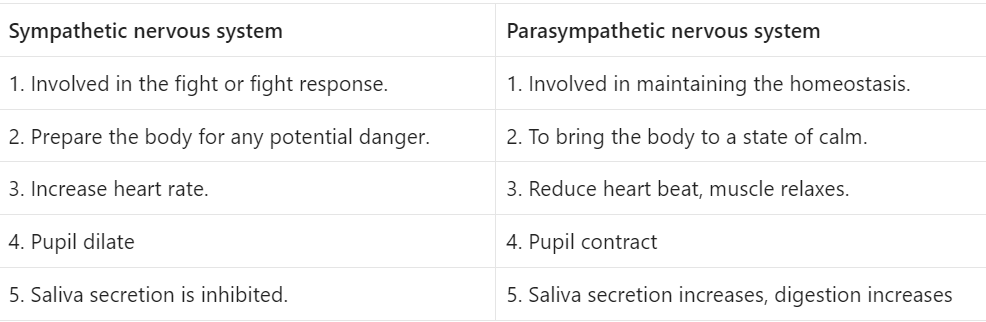
Difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
| Sympathetic nervous system | Parasympathetic nervous system |
| 1. Involved in the fight or fight response. | 1. Involved in maintaining the homeostasis. |
| 2. Prepare the body for any potential danger. | 2. To bring the body to a state of calm. |
| 3. Increase heart rate. | 3. Reduce heart beat, muscle relaxes. |
| 4. Pupil dilate | 4. Pupil contract |
| 5. Saliva secretion is inhibited. | 5. Saliva secretion increases, digestion increases |
Difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system by its properties
| Properties | Parasympathetic nervous system | Sympathetic nervous system |
| Ganglia | Near to organ | Away from organ |
| Preganglionic nerve fiber | Long | Short |
| Neurotransmitter | Acetylcholine | Adrenaline |
| Also known as | Cholinergic | Adrenergic |


To the mimprovement.com administrator, Keep the good content coming!