Table of Contents
Microbiology
The term of microbiology is derived from 2 words: micro and biology. It means the study of life cycle of microorganism is called microbiology. It is the branch of science in which we study about the small living organism which is less than 1 micron. We can’t see with naked eye, they are very small organism like bacteria, virus, protozoa…etc.
The microorganism may be unicellular or multicellular and microorganism found in different-different shapes like spherical, cylindrical, rod shaped and comma shaped. These microorganisms can be seen only with microorganism. This microorganism is Ashish responsible for different disease to human body.
History of microbiology
- 1st time ‘Aristotle’ gave the concept of living and non-living organism.
- In 19th century ‘Roger Bacon’ gave the term disease and it is caused by microorganism.
- ‘Fracastorius’ in 1546 gave the concept of communicable disease, which affect the health person when they come in contact with infected person.
- In 1st concept of living microorganism was given by the ‘Anton-van-Leeuwenhoek’ by in 1675. So, he is known as founder of microbiology, he also gave the term for protozoa and bacteria.
- In 1729 ‘Spallanzani’ prepare the first culture media in which bacteria and virus can be grow.
- Scientist ‘John Tyndall’ say that the microorganism are kills at high temperature, this is called Tyndall effect
- The term microbiology was given by ‘Lewis Pasteur’ and he is also known as father of microbiology. Lewis Pasteur gave the term aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Lewis Pasteur explains that when milk is heated at 62.8° for 30 minutes then all microbes are killing and milk becomes pure, this process is known as pasteurization.
- ‘Lord Joseph Lister’ are giving the concept of use antiseptic before surgery. He is also known as father of antiseptic surgery. He instructed surgeons under his responsibility to wear clean gloves and wash their hand before and after operation with 5% carbolic acid solution.
- ‘Alexander Fleming’ discover the first antibiotic penicillin from fungus. Penicillin was isolated from tobacco leaf.
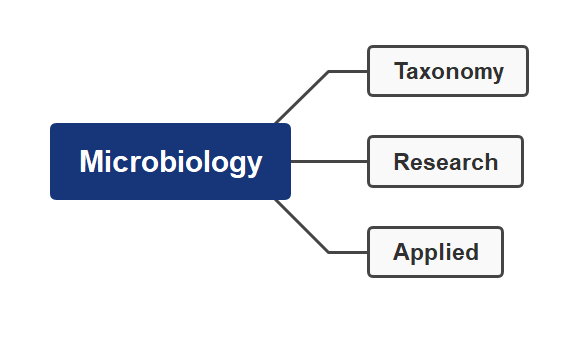
Branches of microbiology
On the basis of their taxonomy, research work and the field where it applied microbiology can be divided into following part:
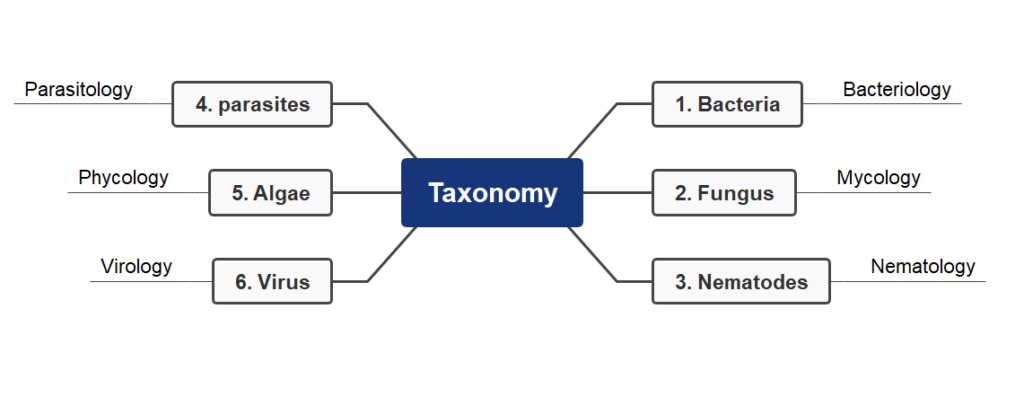
According to “taxonomy”, microbiology is divided into following part:
- Bacteria:- Bacteria are microscopic organisms that can be found in almost every environment on Earth, from soil to water to air. Bacteriology is the study of bacteria and their impact on human health and the environment. They play a vital role in the cycle of life, providing essential nutrients for plants and animals, breaking down organic matter, and even helping to protect us from disease-causing pathogens.
- Fungus:- Mycology is the study of fungi, which are organisms that can be found in almost every environment. Fungi play a vital role in our ecosystems, from providing food and medicine to helping break down organic matter. They also have a wide range of uses in industry and agriculture.
- Nematodes:- Nematology is the study of nematodes, which are microscopic worms that can be found in soil, water, and other environments. Nematodes are important to many ecosystems because they play a role in decomposition and nutrient cycling.
- Parasites:- Parasitology is the study of parasites, which are organisms that live in or on another organism and obtain their nutrition from it. Parasites can cause a wide range of diseases in humans, animals, and plants. They can also affect the environment by altering the balance of species in an ecosystem. This makes parasitology an important field of study for understanding how ecosystems work and how to protect them from parasites.
- Algae:- Algae are a diverse group of organisms that have been studied extensively in the field of psychology. Algae can be used to study the effects of environmental factors on behaviour, as well as how different species interact with each other. They can also be used to explore the effects of light and temperature on behaviour and development. By studying algae, psychologists can gain insight into how different species respond to their environment and how they interact with each other.
- Virus:- Virology is the study of viruses, which are small infectious agents that can cause diseases in humans, animals, and plants. Viruses are made up of genetic material surrounded by a protective coat. They can replicate only inside the cells of other organisms and are responsible for a wide variety of illnesses ranging from the common cold to more serious diseases such as HIV/AIDS and Ebola.
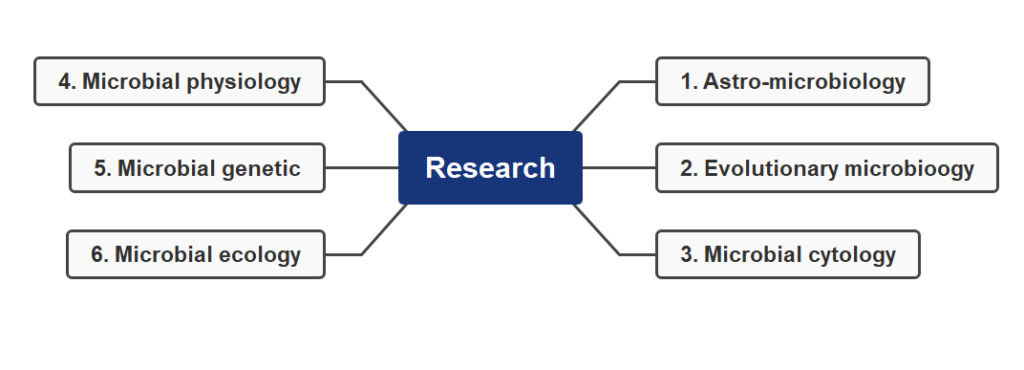
According to “research work”, microbiology is divided into following parts:
- Astro-microbiology
- Evolutionary microbiology
- Microbial cytology
- Microbial physiology
- Microbial genetic
- Microbial ecology
According to “the field where it is applied”, microbiology is divided into following part:
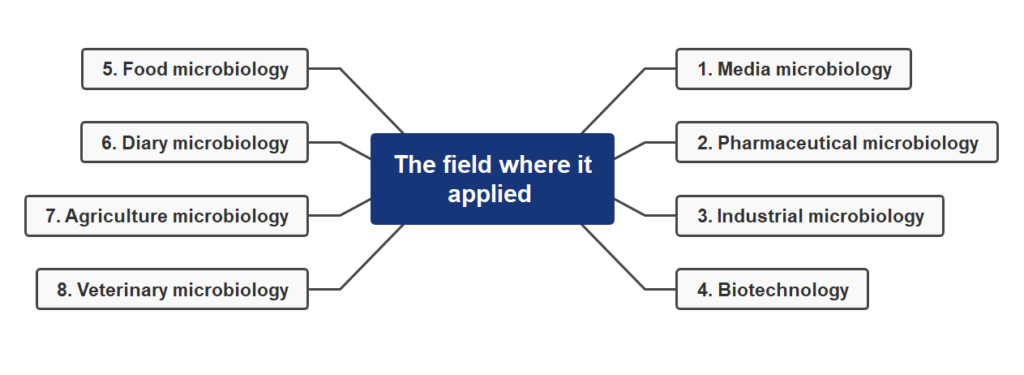
- Medical microbiology
- Pharmaceutical microbiology
- Industrial microbiology
- Biotechnology
- Food microbiology
- Diary microbiology
- Agriculture microbiology
- Veterinary microbiology
- Environmental microbiology