TCA Cycle
In the previous article, you have read about glycolysis in which one molecule of glucose formed by six carbons(6C) in the cytoplasm of the cell is broken down into two molecules pyruvate, a process called glycolysis.
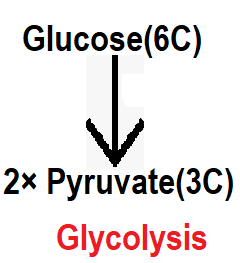
Now we are going to read about TCA cycle which is also known as Krebs cycle. The TCA cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle. The process of this cycle is the oxidation of the acetyl co-enzyme, which leads to the formation of CO2, H2O and ATP. If we talk about basic, then two molecules of pyruvate are formed in the end step of glycolysis, after that pyruvate enters the mitochondria through active transport. The process of the Krebs cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria, where pyruvate cannot reach it directly. Convert pyruvate to an acetyl co-enzyme to enter the Krebs cycle. The acetyl co-enzyme can easily enter the Krebs cycle.
This question is also asked in many exams that what is the joining point of glycolysis and TCA cycle called? So, you should know that the joining point of glycolysis and TCA cycle is called acetyl co-enzyme. When the acetyl co-enzyme enters the Krebs cycle, it is oxidized to form a lot of NADH2, ATP, H2O and CO2, so let’s read the TCA cycle in detail.
Step wise TCA Cycle
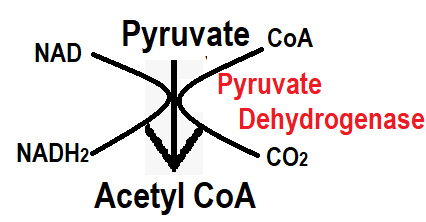
Step-1:- In step 1, when pyruvate enters the mitochondria, pyruvate is converted to acetyl co-enzyme with the help of pyruvate dehydrogenase enzyme. Addition of co-enzyme takes place in this process. When this process occurs, CO2 is reduced and NAD gains hydrogen to form NADH2. NADH2 is further converted into ATP with the help of electron transport chain.
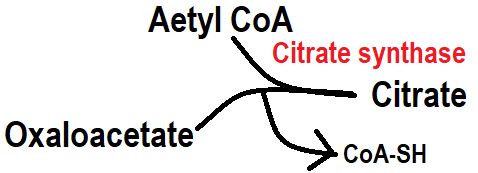
Step 2:- In step 2, oxaloacetate and acetyl co-enzyme combine to form citrate with the help of citrate synthase enzyme. CoA-SH is reduced in this process.
Step 3:- In step 3, citrate is converted to Cis-Aconitase in the presence of aconitase enzyme. In this step the aconitase enzyme removes the water(H2O). You can say that dehydrogenation takes place in this step, hence it is also called reversible step.
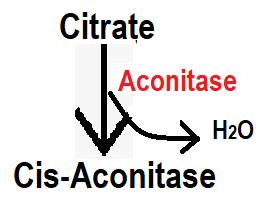
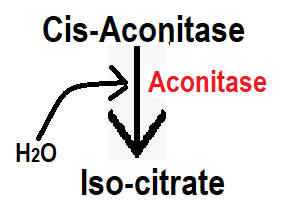
Step 4:- In step 4, Cis-Aconitase converts to Iso-citrate in the presence of aconitase enzyme. Addition of water occurs in this step, so it can be said that rehydrogenation occurs in this step.
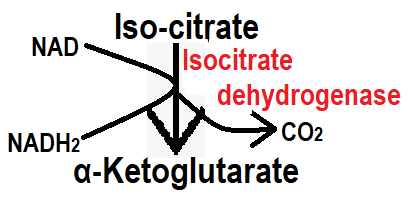
Step 5:- In step 5, iso-citrate is converted to alpha-ketoglutarate with the help of isocitrate dehydrogenase enzyme. In this step, CO2 is reduced and NAD gains hydrogen to form NADH2.
Step 6:- In step 6, alpha-ketoglutarate is converted to Succinyl Co-enzyme in the presence of the alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase enzyme. In this step the enzyme enters CoA-SH and removes CO2. In this step, NAD produce NADH2 by hydrogen gain.
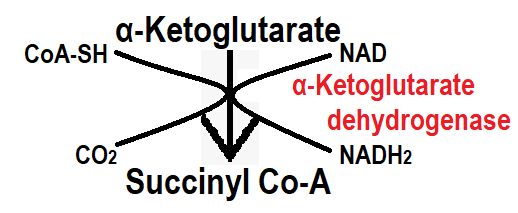
Step 7:- In step 7 the Succinyl Co-enzyme converts to succinate in the presence of Succinyl Co-enzyme synthetase. This enzyme is very important, it converts GDP into GTP and removes Co-SH. This step is also called substrate level phosphorylation.
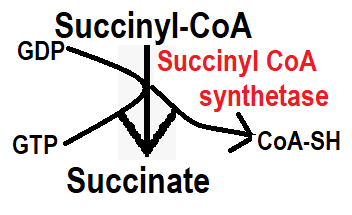
Step 8:- In step 8, succinate is converted to fumarate in the presence of the succinate dehydrogenase enzyme. This step involves the removal of FADH2.
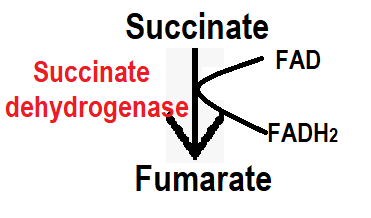
Step 9:- In step 9, with the help of fumarase enzyme, fumarate is converted into malate, in this step water (H2O) is added.
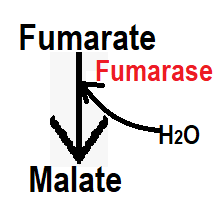
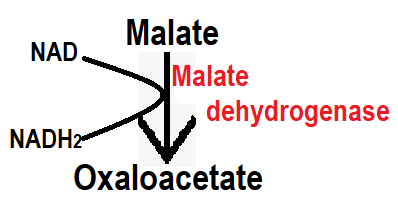
Step 10:- In step 10, malate is converted to oxaloacetate in the presence of the malate dehydrogenase enzyme. There is dehydrogenase in this step so you can understand that it will reduce H+. In this step, NAD produce NADH2 by hydrogen gain.
My next article will be electron transport chain if you liked this article then comment.

Nyc
Dear mimprovement.com administrator, Your posts are always well-received by the community.