Table of Contents
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
The replacement of the hydrogens of the aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons with halogen atoms results in the formation of haloalkanes and haloarenes, where haloalkane also known as alkyl halides and haloarenes also known as aryl halides. In haloalkane, the halogen atoms are sp3 hybridized with the alkyl group, and in haloarenes, the halogen atoms are sp2 hybridized with the aryl group. Now let us read about haloalkanes and haloarenes.
Haloalkanes
Haloalkanes is a combination of two words in which halo refers to halogens which is denoted by ‘X’ (where X = I, Cl, Br, F) and alkanes which means carbons – carbon single bond, whose general formula is CnH2n+2. Basically haloalkanes are replaced with halogens by removing hydrogen. Haloalkanes are denoted by R-X in which R as the alkyl group and X as the halide(F, Cl, Br, F).
Nature of C-X bond
If we talk about the nature of C-X bond, then here C means carbon and X means halogen. The electronegativity of halogen(X) in the C-X bond is very high as compared to the electronegativity of carbon, due to which C-X is polar in nature. Due to the polar bond in C-X, a dipole is generated. Among halogens, fluorine (f) has the highest electronegativity and iodine has the lowest electronegativity.
Method of preparation of alkyl halides
1. Halogenation of Alkane
To obtain alkyl halide from alkane, halogenation of alkane is done in which alkane is reacted with halogen in the presence of sunlight, which leads to the formation of alkyl halide. It is an oxidation reaction. Halogenation of alkane follows free radical chain mechanism.
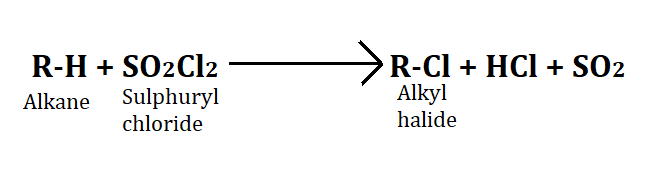
2. Reaction with SO2Cl2(sulphuryl chloride)
Sulphuryl chloride is a very reactive compound. To form alkyl halide from sulphuryl chloride, it is reacted with an alkane. In this process HCl and SO2 gas are released.
3. Hydrohalogenation of alkene(addition of H-X)
Hydrohalogenation of alkene (addition of H-X) is done with the help of alkene to form alkyl halide. The addition of symmetrical alkene can be used to form alkyl halide very easily but addition of unsymmetrical alkene has problems in that case markovnikov’s and anti-markovnikov’s rule is used.

According to markovnikov’s rule the H+ ion will attach where the carbon of the double bond has the highest number of hydrogens. Stability of carbocation is important in markovnikov’s rule. Anti-markovnikov’s reaction is carried out in presence of peroxide which favours homolytic fission. It follows free radical mechanism.
4. Finkelstein reaction
The Finkelstein reaction is completed in the presence of acetone. In this reaction R-Cl is reacted with sodium iodide (NaI) in the presence of acetone to form R-l and sodium chloride(NaCl). You should know that iodine is less reactive as compared to chlorine yet iodine replaces chlorine with the help of acetone. Finkelstein reaction follows SN2 mechanism. With the help of Finkelstein reaction, alkyl iodide is formed.

5. From alcohols
Formation of alkyl halide from alcohols is a very simple method and can be done in several ways, such as when alcohol (R-OH) is reacted with HX, this reaction results in the formation of alkyl halide and water. Similarly, when alcohol (R-OH) is reacted with PX3, an alkyl halide and H3PO3 are formed. There are many more reactions which are given in the below example.
Chemical reaction of alkyl halide
1. Nucleophilic substitution reaction
All alkyl halides show Nucleophilic substitution reaction. Nucleophilic substitution reaction also called SN reactions. In nucleophilic substitution reaction, a nucleophile substitutes X with alkyl halide(R-X) where X is a good living group. Nucleophilic substitution reactions are of two types: SN1 reaction and SN2 reaction.
SN2 reaction:- SN2 reaction is a biomolecular reaction where biomolecular means In this reaction both reagent and substrate are required. This reaction is complete in single step.
During SN2 reaction, inversion of configuration occurs(Walden inversion). Reactivity of alkyl halides toward SN2 mechanism primary halide > secondary halide > tertiary halide, reason; steric hindrance. The reaction rate in the SN2 mechanism depends on the strength of the attacking nucleophile. Non polar solvents strong nucleophiles and high nucleophile concentration support the SN2 reaction. Rearrangement is not possible in SN2 reaction, due to which direct compound formation takes place.
SN1 reaction:- SN1 reaction is an unimolecular reaction where in this reaction unimolecular means only substrate requires for complete the reaction. This reaction is complete in two steps.
The nucleophile present in the SN1 reaction is a very weak nucleophile. The rate of SN1 reaction depends on the halide whereas in SN2 reaction the rate depends on both the nucleophile and the halide. SN1 reaction depends on the stability of carbocation formed. Rearrangement is possible in SN1 reaction whereas rearrangement is not possible in SN2 reaction.
2. Reaction with Grignard reagent
Grignard reagent is an organometallic compound which is highly reactive. Organometallic compound is composed of metal and carbon atom, while carbon atom has negative charge and element has positive charge. If Grignard reagent is reacted with a 1° alkyl halide, then a higher alkane and MgX2 are produced.
Haloarenes
Haloarenes also called aryl halides. Aryl halides are compound where halogen is attached to an aromatic hydrocarbons. Aryl halides may also contain extra substituted compounds. Most important thing, in aryl halides the carbon with which the halogen is attached is sp2 hybridized and the bond with which the halogen attaches to the carbon is strong enough to cause resonance. Aryl halides never show substitution reaction. Aryl halides have the general formula ArX.
Preparation of aryl halides
1. From hydrocarbons
With the help of electrophilic aromatic substitution, we can easily form aryl halides. For example, when benzene is reacted with a halogen in the presence of Fe or AlX3, halobenzene is formed.
2. By Sandmeyer reaction
To form aryl halides by the Sandmeyer reaction, aniline is reacted with sodium nitrite (NaNO2) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) to form benzene diazonium chloride. After the formation of benzene diazonium chloride, it is converted into halobenzene and N2 gas with the help of Gattermann reaction.
Similarly, when benzene diazonium chloride is reacted with potassium iodide (KI), Iodobenzene and nitrogen gas are formed.
3. Balz-schieMann reaction
In the Balz–schieMann reaction, aniline is reacted with sodium nitrite (NaNO2) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) to form benzene diazonium chloride. After which diazonium chloride is reacted with HBF or AsF6 to form fluorobenzene. This whole process is called Balz-schieMann reaction.
With the help of benzene diazonium chloride, benzene can be easily made, in which when benzene diazonium chloride is reacted with hypo-phosphorous acid (H3PO2), then hypo-phosphorous acid reduces diazonium chloride and converts to benzene


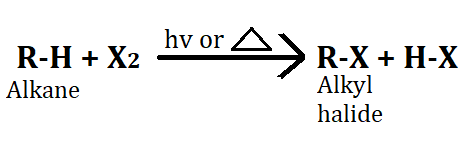
Dear mimprovement.com owner, You always provide great examples and real-world applications, thank you for your valuable contributions.